Introduction
In March 2023, the risk of a wide spread bank contagion shook markets. Hemispheres Investment Management, through it’s global equities and other strategies, capitalized on this turmoil was able to opportunistically invest during this period.
Silicon Valley Bank
Silicon Valley Bank’s (SVB) failure in March brought focus to the financial sector’s stability, triggering a sector-wide stock sell-off. The pandemic, along with Federal Reserve and government responses monetary and fiscal response, increased money supply and liquidity. SVB’s heavy exposure to tech startups and venture capital, combined with reduced risk acceptance due to Federal Reserve rate hikes, led to extreme pressure on the technology and venture capital sectors.
Ready availability of credit to these sectors led to a massive surge in deposits at the bank. Deposits represent liabilities to financial institutions, while assets include loans and securities, in the form of bonds usually. The bonds are held to provide additional earnings for the bank and to meet liquidity and capital needs. The rising interest rates resulted in capital losses on SVB’s bond portfolio, 55% of which was invested in longer maturity securities. SVB sold it’s “available for sale” bonds to meet liquidity requirements, which resulted in a $1.8B loss. The announcement that SVB needed to raise over $2B from equity holders prompted a run on bank deposits, leading to its failure.
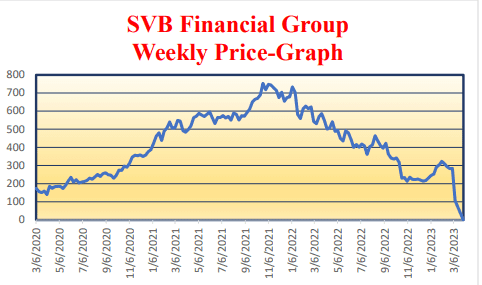
SVB’s unique concentration in tech startups and venture capital, along with its long-term bond allocation, sparked fears of contagion. US regional banks, heavily invested in commercial real estate, suffered. Credit Suisse required rescued through its merger with Union Bank of Switzerland.
Federal Reserve/FDIC Action
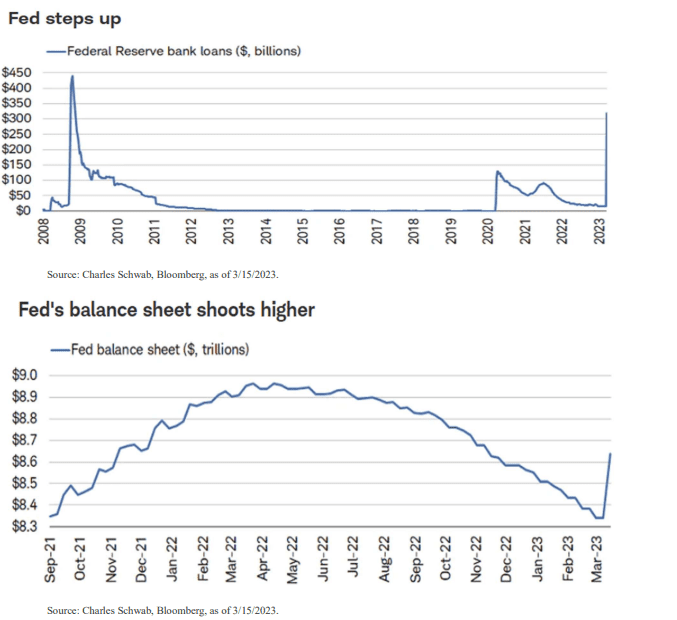
Alongside guaranteeing all SVB deposits (95% exceeding $250k FDIC limits), the Federal Reserve introduced the Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP). This new short-term lending facility assists banks with liquidity needs for up to a year. These measures show the path to financial stability for most banks. Charts on the following page illustrate BTFP lending levels during the month and their impact on the Fed’s balance sheet.
Bank Sector Outlook Near Future
Many banks, maintaining liquidity reserves or borrowing from the Fed, reclassified bonds from “Available for Sale” to “Held to Maturity.” This allows them to hold bonds until maturity, avoiding short-term paper losses on their income statement. Thus, they expect to recover 100% of the face value of these securities over time.
However, this may result in lower profits due to low yields on the bonds in their portfolio. Tighter credit standards are expected in the short-to-intermediate term, but most banks are anticipated to weather the storm.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve’s swift establishment of the BTFP provided over $300 billion in liquidity to banks in March, signaling strong support for the banking sector and averting a larger crisis for now. Despite the risk of recession due to tighter lending standards and higher interest rates, the significant stock price sell-off in the financial sector, including well-capitalized banks, presents an investment opportunity.
Please feel free to contact us with any questions that you may have. Book a meeting
Rebecca Holden, CFA
rholden@hemispheresim.com
Michael A Hart, CFA
April 3, 2023






